Photocatalytic degradation of gentamycin using TiO2 nanoparticle driven by UV light irradiation
Main Article Content
Article Sidebar
Abstract
Antibiotics have been a potential source of life-saving medicines since their discovery. However, because of their widespread usage and poorly enforced restrictions, we now face a new issue: antimicrobial resistance, which poses a worldwide hazard to human and veterinary health. [1,2] India, being a fast expanding and one of the world's most populous country, has overtaken the rest of the world in terms of antibiotic use and production, potentially leading to high antibiotic detection frequencies and concentrations in its environment. Recently, the interest in the environment's dissemination of medicines and the hazards that these medicines pose in highly industrialised nations has increased. [3,4] A wide range of chemicals have been discovered in the steams of river streams and sewage treatment plant effluents on several occasions. These chemicals permeate the aquatic environment in unmodified form following intake and subsequent excretion. [5,6]
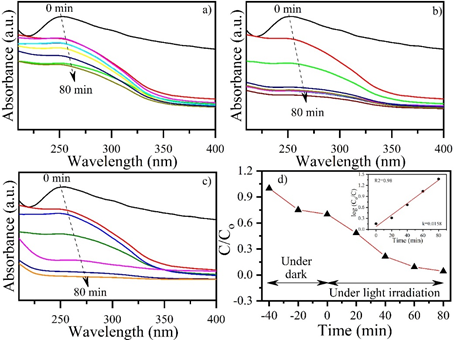
Fig. 1. Photocatalytic degradation study of gentamicin performed in (a) dark, (b) visible light irradiation, (c) UV light irradiation, and (d) show the kinetics plot (C/Co and inset shows the log (Co/C)).
Further research is underway to develop new, fast, and cost-effective environmental protection against antibiotic contamination in wastewater, as well as extensible to control of other reducible pollutants. [7,8] Gentamicin is one of the commonly used antibiotics used to treat pneumonia, meningitis, inflammatory disease, urinary tract infections etc. Overexposure of gentamicin can cause permanent kidney and inner ear problems. Thus, its excessive prescence in the environment is cause of major concern. So, their removal from the environment is important and can be achieved through photocatalysis process. [9,10] The photocatalytic degradation of gentamicin utilizing TiO2nps using visible and UV light has been studied. TiO2nps was synthesized using the co-precipitation method and calcined at 600 °C. Raman study confirmed the phase purity of the material. UV-Vis’s absorption study was performed in which a broad peak was obtained. The photocatalytic study was performed under dark, visible light, and UV light and the corresponding degradation percentage were found to be 54%, 84%, and 96%, respectively. The pseudo-first order reaction rate constant was calculated for the UV light irradiation sample and found to be 0.0158.
How to Cite
Article Details
Gentamicin, TiO2, Nanoparticles, Photocatalysis
2. Hashmi, S. Z. H., Dhiman, T. K., Chaudhary, N., Singh, A. K., Kumar, R., Sharma, J. G., ... & Solanki, P. R. (2021). Levofloxacin Detection Using L-Cysteine Capped MgS Quantum Dots via the Photoinduced Electron Transfer Process. Frontiers in Nanotechnology, 3, 2.
3. Dhiman, T. K., & Singh, S. (2019). Enhanced Catalytic and Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutant Rhodamine‐B by LaMnO3 Nanoparticles Synthesized by Non‐Aqueous Sol‐Gel Route. physica status solidi (a), 216(11), 1900012.
4. Ahlawat, Amit & Rana, Pawan & Solanki, Partima. (2021). Studies of photocatalytic and optoelectronic properties of microwave synthesized and polyethyleneimine stabilized carbon quantum dots. Materials Letters. 130830. 10.1016/j.matlet.2021.130830.
5. Kujur, Vidya & Singh, Satyendra. (2020). Structural, magnetic, optical and photocatalytic properties of GaFeO3 nanoparticles synthesized via non-aqueous solvent-based sol–gel route. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics. 27. 1-14. 10.1007/s10854-020-04318-2.
6. Dhiman, T. K., Lakshmi, G. B. V. S., Dave, K., Roychoudhury, A., Dalal, N., Jha, S. K., ... & Solanki, P. R. (2021). Rapid and Label-Free Electrochemical Detection of Fumonisin-B1 Using Microfluidic Biosensing Platform Based on Ag-CeO2 Nanocomposite. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 168(7), 077510.
7. Dhiman, T. K., Poddar, M., Lakshmi, G. B. V. S., Kumar, R., & Solanki, P. R. (2021). Non-enzymatic and rapid detection of glucose on PVA-CuO thin film using ARDUINO UNO based capacitance measurement unit. Biomedical Microdevices, 23(3), 1-11.
8. AHLAWAT, A., DHIMAN, T. K., Rana, P. S., & Solanki, P. R. (2021). CeO2/TiO2 based nano composite for photocatalytic degradation of Azo-dyes: Nitrophenol and Phenol red. SPAST Abstracts, 1(01).
9. Garimella, L. B., Dhiman, T. K., Kumar, R., Singh, A. K., & Solanki, P. R. (2020). One-step synthesized ZnO np-based optical sensors for detection of aldicarb via a photoinduced electron transfer route. ACS omega, 5(6), 2552-2560.
10. Kumar, R., Lakshmi, G. B. V. S., Dhiman, T. K., Singh, K., & Solanki, P. R. (2021). Highly sensitive amoxicillin immunosensor based on aqueous vanadium disulphide quantum dots. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 892, 115266.
