Irrigation – a potential threat to agriculture?
Main Article Content
Article Sidebar
Abstract
Irrigation is defined as the application of water by an artificial means to land to support the production of crops. Apart from crop production, irrigation also plays an important role in frost protection, suppression of weed growth, and in many other fields [1-3]. Several modern techniques are developed to solve irrigation problems such as an intelligent irrigation scheme, a smartphone irrigation sensor, an IOT based smart irrigation system, a drip irrigation system based on distributed control [4-8]. Although it helps in the cultivation of crops in absence of rain, disadvantages also came along. High initial costs, increase in the concentration of alkaline salts in the soil, loss of water due to evaporation, a chance of waterlogging are some of the demerits [9]. The environment and quality of food production are also being negatively affected by Irrigation [10].
In this work, a design thinking approach was used to find a better solution that is suitable for Indian farmers. The design thinking emphasizes on empathizing with the user and involving the user (farmers) from the beginning of the design process [11]. Based on the developed stakeholders’ map and the empathy map (Fig.1) and the conducted survey, it was evident that farmers were mostly affected due to the negative effects of present irrigation techniques. After, framing various “How might we….” Questions, different ideas were discussed and analysed. Finally, one particular idea was chosen after successful evaluation by using 2 x 2 matrix methods. Later a prototype was developed based on the chosen idea as shown in Fig.2. An innovative concept of early failure was used to test the prototype and collect the feedback of users. The final idea was to come up with a new technique of watering crops inspired by the existing techniques similar to rain-fed irrigation (Fig.3) to overcome some of the demerits of existing irrigation techniques.
With the help of novel design thinking approach a new irrigation technique, an alternative to the present irrigation techniques was developed. It helped in watering plants just like rain does and help in availing the benefits of rain-fed irrigation. It also helped in washing away the toxic substances like chemical fertilizers, pesticides from the plants which contaminate the crop and compromise the quality of the final crop. Feedback was also taken from some of the users. Though the idea is feasible, viable, and useful up to some extent, it should still be improved for better chances of feasibility and viability in the long run.
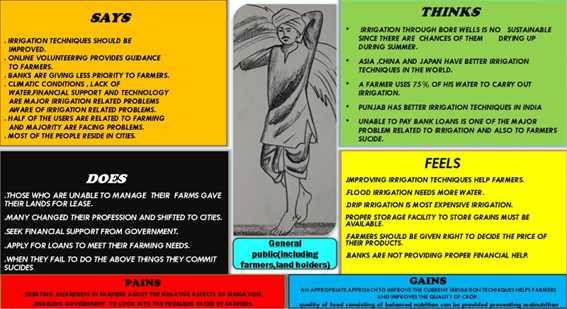
Fig. 1. Empathy Map
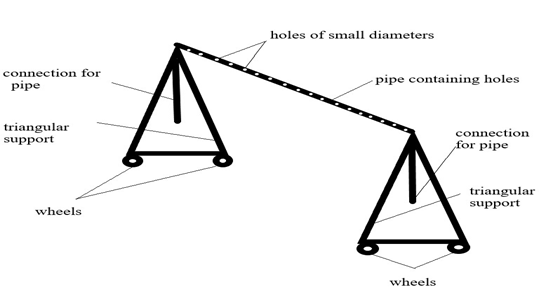
Fig. 2. Sketch of prototype

Fig. 3. Working model
How to Cite
Article Details
Irrigation, soil erosion, waterlogging, smart and intelligent irrigation.
[2] Li. Jingsi, Fei. Liangjun, Li. Shan, Xue. Cai, Shi. Zhongxing, Hinkelmann, Reinhard, “Development of “water-suitable” agriculture based on a statistical analysis of factors affecting irrigation water demand”, Science of the Total Environment, Volume 744(20), 1104- 1117 (2020).
[3] Emad M. Mahmoud, Mohamed M. Nour El-Din, Aiman M. k. El Saadi, Peter Riad, “The effect of irrigation and drainage management on crop yield in the Egyptian Delta: Case of El-Baradi area”, Ain shams Engineering journal, 12(3), 247-254, (2021).
[4] Chen Yuanyuan, Zhang Zuozhuang, “Research and Design of Intelligent Water-saving Irrigation Control System Based on WSN”, IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Applications (ICAICA), (2020).
[5] Joaquín Gutiérrez Jagüey, Juan Francisco Villa-Medina, Aracely López-Guzmán, Miguel Ángel Porta-Gándara, “Smartphone Irrigation Sensor”, IEEE Sensors Journal , 15(9) ,5122 – 5127, (2015).
[6] Goap Amarendra, Sharma Deepak, Shukla A.K., Rama Krishna C., “An IoT based smart irrigation management system using Machine learning and open source technologies”, Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 155, 41-49, (2018).
[7] Yenifer De la Cruz, Camilo Martínez, Andrés Pantoja, “Drip irrigation system based on distributed control — Part 1: Design and model “, IEEE 2nd Colombian Conference on Automatic Control (CCAC), (2015).
[8] Yenifer De la Cruz, Camilo Martínez, Andrés Pantoja, “Drip irrigation system based on distributed control — Part 2: Implementation”, IEEE 2nd Colombian Conference on Automatic Control (CCAC), (2015).
[9] Francisco Pedrero, S. R. Grattan, Alon Ben-Gal, Gaetano Alessandro Vivaldi, “Opportunities for expanding the use of wastewaters for irrigation of olives”, Agricultural Water Management, Volume 241, 912-920 (2020).
[10] Liu Yuan, Hu Chao, Li Baogui, Ding Dawei, Zhao Zhijuan, Fan Tao, Li Zhongyang, “Subsurface drip irrigation reduces cadmium accumulation of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) plants in upland soil”, Science of The Total Environment, 755(2), 5803-5824 (2021).
[11] Brown T., & Kātz B., “Change by design: How design thinking transforms organizations and inspires innovation”. Chicago (15th ed.), 2009.
