Auditron – An IoT based Smart Audit System for Monitoring Electricity and Water Consumption
Main Article Content
Article Sidebar
Abstract
In today’s scenario, water and electricity consumption are at an all-time high. We use these commodities on a daily basis but never bother to analyse and track their usage. In some cases, the large fluctuation in the usage of these commodities may cause inconveniences in finances [1].
The average electricity consumption of households in the city of Bangalore is around 300 kWh per month. The average water consumption of households in Bangalore is 150 litres per person every day. Considering a family of 3 people, this amounts to around 4500 litres of water per person per month.
These consumption amounts are very concerning especially in an ever-growing city like Bangalore. Owing to the digital revolution, we can see a sharp increase in the electricity consumption of households across the world. Due to the growing population every year, the demand for water has drastically increased. However, the amount of water discharged into the freshwater bodies (into consumable water sources for humans) is less than the amount required by the population. In order to regulate and manage the usage of these resources, we are proposing an idea on an Audit system using Internet of Things (IoT) Technology.
The main control unit of this project is the NodeMCU which uses the NodeMCU microcontroller chip. The project consists of two electronic subsystems: one for water level management and the other for electricity consumption management. Both these setups will use separate sets of hardware components embedded into one integrated system. The outputs will be shown via LCD displays and also on the IoT platform. The flowchart in Fig 1 depicts the functioning of the proposed model.
The electricity management system measures the current usage using a non-invasive AC current clamp sensor. This displays the output in terms of watts and amperes used. These readings will be sent to the user using SMS (Short message service ) via a GSM (Global system for mobile communication) module [2]. We will also be adding a cost window on the IoT platform to analyse the monthly expenditure of the user [3]. On the other hand, the water level system works with the help of probes connected to various resistors that measure the water level by passing current and display it in terms of percentage of the tank filled. This percentage value will be displayed via a gauge [4] using the Blynk IoT application so that the user will be provided with a visual representation of the amount of water used.
Some of the major challenges we are anticipating are as follows. Firstly, we will need to convince people about the advantages of having such an audit system in their homes. This includes educating them about the current crisis we are facing and about the role they can play in order to avoid it. Secondly, we will need to deal with the installations and regular maintenance of the device in potentially thousands of households across the country. This will require great manpower, technical expertise and an organized structure.
Our innovation in the design of existing energy meters is that our device consists of an option to set a particular number of units for consumption every day. This can be done by either setting up the total expenditure the user wants per month or by setting the number of units the user wants to consume every month. Similarly, the user can track their water consumption on a daily basis and will be more likely to only consume the necessary amount of water. This will make sure that the users are conscious about their usage of these resources and can make immediate changes to their habits.
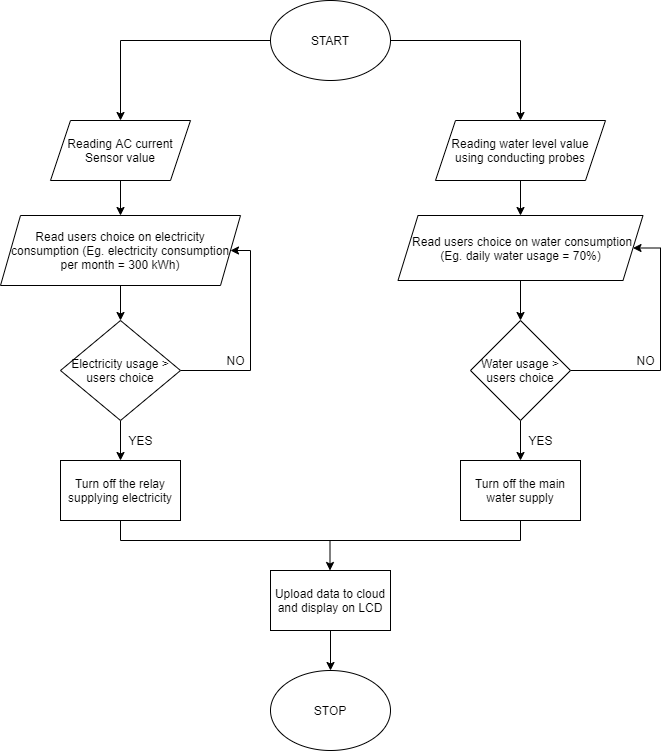
Fig.1. Flowchart of the proposed smart model
How to Cite
Article Details
Audit system, IoT, NodeMCU, GSM, Electricity, Water, Energy meter
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.08.019
[2] Santhosh, Chella & S V, Aswin & Krishna, J. & Vaishnavi, M. & Sairam, P. & Kasulu, P.. (2021). IoT based smart energy meter using GSM. Materials Today: Proceedings. 46.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.02.641
[3] Avancini, D.B., Rodrigues, J., Rabêlo, R., Das, A., Kozlov, S., & Solic, P. (2020). A new IoT‐based smart energy meter for smart grids. International Journal of Energy Research, 1, 1-14.
https://doi.org/10.1002/er.5177
[4] L. S. P. Sairam Nadipalli, D. Sai Akhil, A. A. Kumar and N. Ganesh. Water Conservation Control by using IoT Smart Meter. 2021 5th International Conference on Computing Methodologies and Communication (ICCMC), 2021, pp. 448-452.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCMC51019.2021.9418251
