Molecular scale lamellar structure control in comb-shaped random copolymers
Main Article Content
Article Sidebar
Abstract
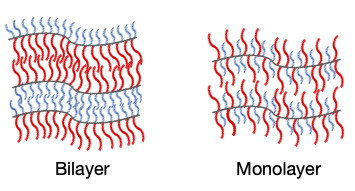
Block copolymers, which consist of two homopolymers with different chemical properties tethered together formed unique self-assembled structure such as lamellae, cylinder, sphere etc. by microphase separation between each block. It has been experimentally and theoretically revealed that the phase behavior of diblock copolymers depended of χ×N and φ, where χ is the Flory–Huggins segmental interaction parameter, N the degree of polymerization and φ1 the volume fraction of one block.1-4 On the other hand, recently, we and other groups reported that homopolymers and random copolymers also formed a self-assembled structure by phase separation. We have reported that homo and random copolymers of poly(alkyl acrylamide) and poly(alkyl acrylate) formed a highly oriented lamellar structure by annealing under humid condition. It has been concluded that segregation between water adsorbed main chain and alkyl side chains (nanophase separation) is the driving force for the lamellar structure formation. Terashima et al. reported that random copolymer of octadecyl acrylate with oligo ethylene glycol formed a lamellar structure by phase separation between crystalized octadecyl chains and oligo ethylene glycol chains. Furthermore, Nagno et al., has reported order of mesogen in side chain liquid crystal polymer increase with addition of non-mesogenic comonomer. They concluded that segregation between the mesogenic and non-messogenic groups Indeed, we have reported addition of hydrophilic comonomer to the alkyl acrylamide . These reported works indicate that self-assembled structure can be formed even in random copolymers by segregation between main chain and side chain and/or comonomers. The main chain of random copolymer formed the lamellar plane whereas the side chains orient perpendicularly to the lamellar plane. Thus, two types of lamellar structure; alkyl side chains oriented both direction to the main chain (homo lamellar) or that orient one direction and other comonomer orient to the other (hetero lamellar). In this paper, we reported that the homo and hetero lamellar depended on the ratio of comonomer. Moreover, order to order transition; hetero to homo lamellar was demonstrated by changing the annealing condition. The present result suggested that self-assembled structure of random copolymer also depended on φ of comonomer. In this lamellar structure two types of lamellar structure can be formed from random copolymer; homo and hetero segregated lamellar.
How to Cite
Article Details
2. L. Leibler, "Theory of Microphase Separation in Block Copolymers", Macromolecules 13, 1602-1617 (1980).
3. F. S. Bates and G. H. Fredrickson, "Block Copolymers—Designer Soft Materials", Phys. Today 52, 32-38 (1999).
4. H. W. Ian, The Physics of Block Copolymers. (Oxford Science, New York, 1999).
