Study of the removal of basic blue-41 from simulated wastewater by activated carbon prepared from discarded jute fibre
Main Article Content
Article Sidebar
Abstract
Dye polluted wastewater generated by a number of industries e.g., textile, paper, food, cosmetics, leather, pharmaceuticals, etc. is detrimental to the environment and living creatures. As a consequence, the contamination of environmental water bodies is becoming a growing concern amongst environmentalists and civilians. To address this problem, a long-term sustainable and efficient dye effluent treatment method should be developed. To date different physical, chemical and biological treatment techniques have been proposed. Chemical and biological techniques are restricted due to their high investment and functional costs. On the other hand, physical methods like ion exchange and reverse osmosis are useful because of the efficient removal of contaminants from industrial wastewater, but their usage on a large scale is limited due to their high capital and operating costs. Among the available methods for the treatment of wastewater, adsorption demonstrates a potential strategy for this purpose [1]. Adsorption is more advantageous than other available methods due to its low capital, operation, and design costs [2]. Some recent researches proposed activated carbon (AC) from different bio-sources has proved its excellent candidacy as an adsorbent for decontaminating wastewater due to its high surface area, low cost, and biodegradability [3]. Herein, we report inexpensive and abundant jute fibre as an efficient precursor for the fabrication of AC. The AC has been synthesized from jute fibre by H3PO4 acid-hydrolysis and the activation of the materials is carried out with the help of KOH. In addition to the chemical activation, thermal activation under air has also been introduced. Due to the facile synthesis route using thermochemical methods a large number of pores are expected to be introduced in the produced carbon material. The sample was named as activated carbon from jute fibre (AC-JF), which was used for batch adsorption study for the removal of an industrial toxic dye, basic blue 41 (BB41). The dependence of the adsorption process on different factors e.g., pH, contact time, and initial strength of dye solution has been investigated to find the optimum process parameters and represented in Fig.1. The optimum pH was found to be 7. The adsorption was rapid for the first 30 minutes and reaches equilibrium at 80 minutes of contact time as the active sites of the adsorbent get saturated with time. Initially, the adsorption increased with time due to strong adsorbent-adsorbate interaction and reached a maximum value of 156.6 mg/g. Adsorption kinetics were interpreted by pseudo-1st and 2nd order kinetics, and it was best described by the later one. The maximum removal percentage was about 89%, and an adsorption capacity of around 160 mg/g was calculated from Langmuir isotherm, which supports the experimental value. This extensive study of the nature of the adsorption process revealed the usability and suitability of AC-JF as a prominent adsorbent for the removal of organic pollutants from wastewater.
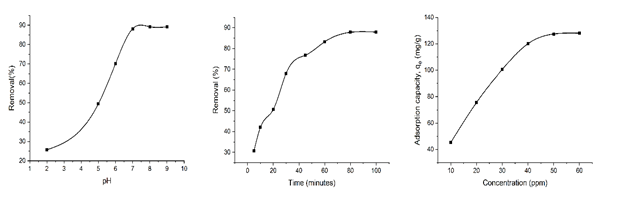
Fig.1. Effect of pH, time, and concentration on adsorption process.
How to Cite
Article Details
Jute fibre; activated carbon; biodegradability; thermochemical; wastewater treatment; kinetics, isotherm.
2. Rahman, E., et al., The seed of Burmese grape (BACCAUREA RAMIFLORA) as low-cost bio-adsorbent for removal of methylene blue from wastewater. 2020.
3. El maguana, Y., et al., Activated Carbon for Dyes Removal: Modeling and Understanding the Adsorption Process. Journal of Chemistry, 2020. 2020: p. 2096834.
